In the ever-expanding world of cannabis products, two intriguing options have gained the attention of the masses: hemp seed oil and hemp-derived CBD oil. While they share the same source – the hemp plant (Cannabis sativa) – these oils have distinctly different compositions, applications, and potential benefits.
Let’s explore the differences between Hemp Seed Oil vs. Hemp-Derived CBD Oil in order to equip you with valuable information to make informed choices.
- Hemp Seed Oil (HSO): A Nutrient-Rich Dietary Addition
- CBD Oil: Unlocking Cannabinoid Potential
- Conclusion: Empowering Informed Choices

Hemp Seed Oil: A Nutrient-Rich Dietary Addition
Hemp seed oil is a natural oil derived from the seeds of the hemp plant (Cannabis sativa). It is prized for its rich nutritional profile and versatility. It is known for its well-balanced ratio of essential fatty acids, particularly omega-3 and omega-6,1,2 making it a valuable addition to both dietary and skincare routines.
This oil is often used as a dietary supplement,1,2 salad dressing, cooking oil, and an ingredient in skincare and cosmetic products due to its moisturizing and soothing properties.3 It does not contain significant levels of cannabinoids like CBD or THC and is typically consumed for its nutritional benefits and skin-soothing qualities.
Nutritional Profile
Hemp seed oil is renowned for its exceptional nutritional content,4 packed with a variety of essential nutrients that contribute to overall health and well-being.
Here’s a nutritional content profile for hulled hemp seed from the USDA,5 which gives a fair approximation of the nutritional content of hemp seed oil.
When compared to the nutritional content profile from Nutrition & Metabolism on PubMed Central, it reflects that much of the nutritional value is lost by removing the hulls from the equation.6

Serving Size: 3 tablespoons 30 grams
Calories: Approximately 166 calories
Fats:
- Total Fat: Approximately 14.6 g
- Saturated Fat: Approximately 1.4 g
- Monounsaturated Fat: Approximately 1.6 g
- Polyunsaturated Fat: Approximately 11.4 g
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Approximately 1.4 g
- Omega-6 Fatty Acids: Approximately 5.5 g
- Approximate Omega-6:Omega-3 fatty acid proportion 3:1 (considered optimal)
Vitamins:
- Vitamin E (Alpha-Tocopherol): Approximately 0.24 mg (5% of the DV)
- Vitamin B-6: Approximately 0.2 mg (26% of the DV)
- Thiamin: Approximately 0.4 mg (33% of the DV)
- Niacin: Approximately 2.75 mg (17% of the DV)
Minerals:
- Phosphorus: Approximately 495 mg (20% of the DV)
- Potassium: Approximately 360 mg (7% of the DV)
- Magnesium: Approximately 210 mg (50% of the DV)
- Zinc: Approximately 3 mg (33% of the DV)
- Copper: Approximately 0.5 mg (56% of the DV)
- Manganese: Approximately 2.3 mg (100% of the DV)
NOTE: These contents can vary widely over different growing conditions, strains, and cultivars.

Antioxidants and Phytochemicals:
- Tocopherol: A specific form of vitamin E that acts as a potent antioxidant.
- Phytosterols: Plant compounds with potential cholesterol-lowering properties.
- Polyphenols: While not as concentrated as in some fruits and vegetables, hemp seed oil does contain polyphenolic compounds with antioxidant properties.
- Terpenes: Aromatic compounds that contribute to the flavor and scent of hemp seed oil.
Please note that the nutritional content of hemp seed oil can vary greatly based on factors such as the processing method, the specific brand or product, the growing conditions, and the strain or cultivar of the hemp plant.
Nevertheless, hemp seed oil remains an excellent source of essential fatty acids, particularly omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids and essential amino acids. It’s a valuable addition to a balanced diet, especially for those seeking to enhance their intake of these essential nutrients.
Hemp Seed Oil Benefits
Hemp seed oil is celebrated for its array of potential health benefits, thanks to its rich nutritional profile. While it doesn’t contain significant levels of cannabinoids like CBD or THC, it is packed with essential nutrients and bioactive compounds that contribute to overall well-being. Here are some of the potential benefits of hemp seed oil:
Heart Health: Hemp seed oil is known for its ideal balance of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids.1-6 Consuming these fatty acids in the right proportion may help support cardiovascular health by promoting healthy cholesterol levels and maintaining proper blood vessel function.7,8
Skin Health: Hemp seed oil is often used in skincare products9 for its moisturizing and soothing properties.2,10 It can help alleviate dry skin, reduce redness, and promote healthy-looking skin.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: The presence of phytol and other compounds in hemp seed oil gives it potential anti-inflammatory properties.11,12 This can be beneficial for conditions characterized by chronic inflammation, such as arthritis.
Brain Health: Omega-3 fatty acids,1-6 including alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), are essential for brain health and function. Consuming hemp seed oil may support cognitive health and reduce the risk of cognitive decline.
Immune System Support: The combination of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants in hemp seed oil can help support a robust immune system,13,14,15 helping the body fend off infections and illnesses.
Balanced Nutrition: Incorporating hemp seed oil into your diet can help you achieve a balanced intake of essential nutrients, particularly if you have dietary restrictions or preferences.
Hormone Regulation: GLA in hemp seed oil may help regulate hormonal imbalances and alleviate symptoms associated with conditions like premenstrual syndrome (PMS).16-19
Joint Health: Some individuals use hemp seed oil for its potential to reduce joint discomfort and promote joint health,20,21,22 particularly in cases of mild arthritis.
Overall Wellness: Hemp seed oil can be viewed as a holistic dietary supplement, contributing to overall well-being by supplying essential nutrients and beneficial compounds.
It’s important to note that while hemp seed oil offers potential health benefits, individual responses may vary. It’s advisable to consult with a healthcare provider or registered dietitian before making significant dietary changes, especially if you have specific health concerns or are taking medications.
Additionally, choosing high-quality, cold-pressed hemp seed oil can help maximize its nutritional benefits.
HSO Uses
Hemp seed oil is a versatile product with a wide range of potential uses, both for dietary and topical applications. Here are some common uses of hemp seed oil:

Dietary Uses:
Nutritional Supplement: Hemp seed oil is often consumed as a dietary supplement due to its rich nutritional profile. It provides a balanced ratio of essential fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals.23,24
Food Additive: Hemp seed oil can be used as a food additive in virtually any foodstuff like salad dressing, cooking oil, or added to any food or drink.

Topical Uses:25
Skincare: Hemp seed oil is commonly used in skincare products due to its moisturizing and soothing properties. It may help alleviate dry skin, reduce redness, and soothe irritation.10
Massage Oil: Hemp seed oil’s smooth texture and moisturizing capabilities make it an excellent choice for massage oil.
Hair Care: Some people use hemp seed oil as a hair conditioner26,27 or mask to improve hair health and manage frizz.
Lip Balm: Apply a small amount of hemp seed oil to chapped lips for natural hydration and relief.
Nail and Cuticle Oil: The use of hemp seed oil may moisturize and strengthen nails and soften cuticles.

Diverse HSO Products
Hemp seed oil is a versatile product with a range of uses, and it’s available in various forms and products to suit different needs and preferences. Here’s a brief overview of the hemp seed oil product range:
Pure Hemp Seed Oil: Bottled hemp seed oil in its purest form, typically available in various sizes. It can be used for cooking, as a dietary supplement, or for topical applications.
Capsules: Pre-measured doses of hemp seed oil in convenient capsule form. Capsules are an easy way to incorporate hemp seed oil into your daily routine.
Softgels: Similar to capsules, softgels contain pre-measured amounts of hemp seed oil. They are easy to swallow and can be taken with or without food.
Salves and Balms: Topical products infused with hemp seed oil for skin care and localized relief. They are used to soothe dry skin, reduce redness, and alleviate muscle or joint discomfort.
Shampoos and Conditioners: Hair care products that contain hemp seed oil to promote healthy hair and scalp, reduce frizz, and add shine.
Lotions and Creams: Moisturizing skin care products infused with hemp seed oil for overall skin health. They can help with dry skin, eczema, and other skin conditions.

Massage Oils: Massage oils that are made with hemp seed oil for a soothing and relaxing massage experience.
Lip Balms: Lip balms infused with hemp seed oil to provide hydration and relief for chapped lips.
Pet Supplements: Dietary supplements made with hemp seed oil, designed to support the health and well-being of pets, particularly for their skin and coat.
Cooking Oil: Hemp seed oil, specifically marketed as a cooking oil. It can be used in salad dressings, as a drizzle over cooked dishes, or as a dip for bread.
Face Serums: Face serums infused with hemp seed oil for skincare routines, with a focus on reducing redness, moisturizing, and soothing skin.
Massage Candles: Candles that melt into warm massage oil when lit, containing hemp seed oil for relaxation.
Soap: Handmade or commercially produced soap bars that incorporate hemp seed oil for its moisturizing and skin-soothing properties.
Keep in mind that the availability of these products may vary depending on your location and local regulations. It’s essential to choose reputable brands that provide high-quality, cold-pressed hemp seed oil to maximize the nutritional benefits and effectiveness of the products you select.

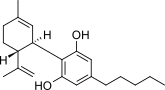
CBD Oil: Unlocking Cannabinoid Potential
CBD (cannabidiol) oil is a natural extract derived from the hemp plant (Cannabis sativa). It is celebrated for its potential therapeutic benefits thanks to its interaction with the body’s endocannabinoid system. Unlike THC, CBD is non-psychoactive, meaning it doesn’t produce a “high.” Instead, it is used for its potential to alleviate various health concerns, such as pain, anxiety, and inflammation.28
CBD oil comes in various forms, including tinctures, capsules, edibles, and topicals, making it versatile and suitable for different applications. Users often incorporate it into their wellness routines to promote relaxation, reduce discomfort, and enhance overall well-being.

Therapeutic Potential of CBD
Hemp-derived CBD (cannabidiol) oil has garnered significant interest for its potential therapeutic benefits. While research is still ongoing, numerous studies and anecdotal reports suggest that CBD oil may offer various therapeutic applications. Here are some of the potential therapeutic benefits of hemp-derived CBD oil:
Pain Management: CBD has been studied for its potential to alleviate various types of pain, including chronic pain conditions, neuropathic pain, and pain associated with inflammatory disorders. It may interact with receptors in the endocannabinoid system and other pathways to modulate pain perception.29,30
Anxiety and Stress Reduction: CBD has shown promise in reducing anxiety symptoms and mitigating stress.31-34 Many users report feeling calmer and more relaxed after taking CBD oil. It may affect the brain’s receptors for serotonin, a neurotransmitter associated with mood regulation.
Epilepsy and Seizure Disorders: Epidiolex, a prescription CBD medication, has received FDA approval for the treatment of specific forms of epilepsy, including Dravet syndrome and Lennox-Gastaut syndrome. CBD’s anticonvulsant properties are well-documented.35-40

Neuroprotection: CBD has been investigated for its potential to protect nerve cells and support brain health. It may have neuroprotective properties that could be beneficial in neurodegenerative conditions like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease.41-46
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: CBD exhibits anti-inflammatory properties,47,48 which may be useful in conditions characterized by excessive inflammation, such as arthritis and autoimmune disorders.
Antioxidant Properties: CBD acts as an antioxidant, helping to combat oxidative stress and protect cells from damage caused by free radicals.48
It’s important to note that the effectiveness of CBD oil can vary from person to person, and its potential therapeutic benefits are not guaranteed for everyone.
Additionally, CBD products vary in terms of quality and dosage, so it’s essential to choose high-quality products and consult with a healthcare provider before using CBD oil, especially if you have specific medical conditions or are taking other medications.
Always start with a low dose and gradually increase it while monitoring how your body responds.
As research on CBD continues, more insights into its therapeutic potential and specific applications are likely to emerge. It’s an evolving field with exciting possibilities for various health concerns.

CBD Uses
CBD, or cannabidiol, is utilized for various purposes, including stress reduction, enhanced sleep, mood balance, improved focus, energy enhancement, digestive comfort, appetite regulation, potential immune support, skin health, and overall well-being. It’s commonly integrated into daily routines to promote a sense of balance and well-being.
Enhanced Sleep: CBD may support better sleep quality and help regulate sleep patterns. Broad or Full-Spectrum CBD that contains terpenes with sedative properties like Myrcene or Linalool are best for inducing sleep.49-52
Mood Balance: Some individuals use CBD to help maintain emotional well-being and a positive outlook.53,54,55
Focus and Mental Clarity: CBD is said to potentially enhance mindfulness, concentration, and mental clarity. There is very limited research to support these claims.56
Digestive Comfort: CBD may contribute to a healthy digestive system and alleviate digestive discomfort.57,58,59
Appetite Regulation: CBD can assist in regulating appetite, potentially benefiting those with appetite-related concerns.60,61,62
Immune System Support: There’s a belief among some that CBD may provide support for the immune system.63,64,65
Skin Health: Topical CBD oil is used to promote healthy skin, reduce redness, and address skin conditions.66-69
Overall Well-Being: Many people incorporate CBD oil into their daily routines to support general well-being and a balanced lifestyle.
It’s important to remember that individual responses to CBD may vary, and it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare provider before using it for specific health concerns. Additionally, ensure that you choose high-quality CBD products from reputable sources and adhere to recommended dosing guidelines.

Diverse CBD Products:
The product range of hemp-derived CBD (cannabidiol) is diverse and continually expanding to meet the demands and preferences of consumers. CBD products come in various forms and delivery methods, allowing individuals to choose the option that best suits their needs and preferences. Here is an overview of the common product categories within the CBD market:
Sublingual Tinctures: CBD oil tinctures are designed for sublingual (under the tongue) use. They typically come with a dropper for precise dosing. Users place a few drops under the tongue and hold them for a minute or two for fast absorption. Tinctures are versatile and can be used to address a wide range of concerns.
CBD Capsules and Softgels: Pre-measured doses of CBD oil in capsule or softgel form. They offer convenient and consistent dosing and are suitable for individuals who prefer a familiar pill format for supplementation.
Edibles: CBD-infused edibles include gummies, chocolates, candies, and beverages. These products provide a tasty and discreet way to consume CBD. Effects may take longer to kick in compared to sublingual administration.
Topical Balms and Creams: CBD-infused skincare products like balms, creams, and lotions are designed for topical application. They are used to soothe localized discomfort, reduce inflammation, and improve skin health.
Vape Products: Vaporizable CBD products, including vape pens, e-liquids, and cartridges, are inhaled for rapid absorption. Vaping offers a fast-acting method of delivery but comes with potential health risks associated with inhaling.
Isolate Powders: CBD isolate is a crystalline form of pure CBD, containing no other cannabinoids or compounds from the hemp plant. It can be used to create custom CBD products, added to foods, or mixed with other supplements.

Full-Spectrum and Broad-Spectrum Products: These products contain a range of cannabinoids, terpenes, and other beneficial compounds from the hemp plant. Full-spectrum products include trace amounts of THC (below the legal limit), while broad-spectrum is THC-free. They are believed to offer enhanced therapeutic benefits due to the “entourage effect.”
Pet Products: CBD products formulated for pets, including oils, treats, and capsules, are used to support the health and well-being of animals. They may help alleviate anxiety, pain, and other issues in pets.
Beverage Additives: CBD additives like water-soluble tinctures or powders can be added to beverages like tea, coffee, or smoothies for easy consumption.
Concentrates and Dabs: Highly concentrated CBD extracts designed for vaporization or dabbing are used by experienced users seeking potent and fast-acting effects.
Suppositories: CBD suppositories are designed for rectal or vaginal use and provide an alternative method of CBD administration for specific conditions.
Transdermal Patches: Adhesive patches infused with CBD provide a slow and consistent release of CBD through the skin for an extended period.
Beauty and Cosmetics: CBD is incorporated into various beauty and cosmetics products such as serums, masks, and creams, with a focus on promoting skin health and reducing inflammation.

The CBD market is continually evolving, with new product innovations regularly emerging. Consumers should research products carefully, consider their individual needs and preferences, and ensure that they purchase from reputable companies that provide third-party lab testing results for product quality and cannabinoid content.
Additionally, it’s important to be aware of local regulations regarding the sale and use of CBD products.
Conclusion: Empowering Informed Choices
In wrapping up the conversation, hemp seed oil and hemp-derived CBD oil cater to diverse needs and offer distinct advantages. Hemp seed oil is a nutritional powerhouse, enhancing overall nutrition with its well-rounded fatty acid composition and comprehensive nutrient profile.
On the other hand, hemp-derived CBD oil holds promise for targeted relief from specific health concerns, thanks to its potential therapeutic applications.
Rather than framing this as a choice between the two, it’s important to understand the unique benefits each offers. Hemp seed oil bolsters overall nutrition, while CBD oil may provide tailored solutions for particular conditions.
Ultimately, your selection should align with your specific wellness goals. Consulting with a healthcare professional can help guide your decision, ensuring it complements your individual requirements and preferences.
As research continues to uncover the nuances of these oils, consumers are empowered to make informed choices to optimize their health and well-being.
 RL Williams, AKA Chronic RL
RL Williams, AKA Chronic RL
“Exploring a Greener Path: Navigating Cannabis, CBD, and Advocacy with a Chronic Passion” See About Info, and other articles from RL
References:
1. Cerino P, Buonerba C, Cannazza G, D’Auria J, Ottoni E, Fulgione A, Di Stasio A, Pierri B, Gallo A. A Review of Hemp as Food and Nutritional Supplement. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2021 Feb 12;6(1):19-27. doi: 10.1089/can.2020.0001. PMID: 33614949; PMCID: PMC7891210. PubMed Central. Accessed 14 Oct. 2023.
2. WebMD Editorial Contributors. Medically Reviewed by Christine Mikstas, RD, LD on March 07, 2023 “Health Benefits of Hemp Seed Oil.” WebMD, 23 Dec. 2020. Accessed 14 Oct. 2023.
3. Cerino P, Buonerba C, Cannazza G, D’Auria J, Ottoni E, Fulgione A, Di Stasio A, Pierri B, Gallo A. A Review of Hemp as Food and Nutritional Supplement. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2021 Feb 12;6(1):19-27. doi: 10.1089/can.2020.0001. PMID: 33614949; PMCID: PMC7891210. PubMed Central. Accessed 14 Oct. 2023.
4. Montero L, Ballesteros-Vivas D, Gonzalez-Barrios AF, Sánchez-Camargo ADP. Hemp seeds: Nutritional value, associated bioactivities and the potential food applications in the Colombian context. Front Nutr. 2023 Jan 11;9:1039180. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1039180. PMID: 36712539; PMCID: PMC9875026. Accessed 14 Oct. 2023.
5. FoodData Central. Usda.gov. Published 2023. Accessed October 16, 2023.
6. Rodriguez-Leyva D, Pierce GN. The cardiac and haemostatic effects of dietary hempseed. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2010 Apr 21;7:32. doi: 10.1186/1743-7075-7-32. PMID: 20409317; PMCID: PMC2868018. Accessed October 16, 2023.
7. Simopoulos AP. The importance of the ratio of omega-6/omega-3 essential fatty acids. Biomed Pharmacother. 2002 Oct;56(8):365-79. doi: 10.1016/s0753-3322(02)00253-6. PMID: 12442909. Accessed October 16, 2023.
8. DiNicolantonio JJ, O’Keefe J. The Importance of Maintaining a Low Omega-6/Omega-3 Ratio for Reducing the Risk of Autoimmune Diseases, Asthma, and Allergies. Mo Med. 2021 Sep-Oct;118(5):453-459. PMID: 34658440; PMCID: PMC8504498. Accessed October 16, 2023.
9. NIVEA. Hemp Seed Oil Benefits for Skin. Nivea.com.au. Published December 6, 2021. Accessed October 16, 2023.
10. Martins AM, Gomes AL, Vilas Boas I, Marto J, Ribeiro HM. Cannabis-Based Products for the Treatment of Skin Inflammatory Diseases: A Timely Review. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Feb 9;15(2):210. doi: 10.3390/ph15020210. Erratum in: Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Jul 11;15(7): PMID: 35215320; PMCID: PMC8878527. Accessed October 16, 2023.
11. WebMD Editorial Contributors. Medically Reviewed by Christine Mikstas, RD, LD on March 07, 2023 “Health Benefits of Hemp Seed Oil.” WebMD, 23 Dec. 2020, Accessed 16 Oct. 2023.
12. Claro-Cala CM, Grao-Cruces E, Toscano R, Millan-Linares MC, Montserrat-de la Paz S, Martin ME. Acyclic Diterpene Phytol from Hemp Seed Oil (Cannabis sativa L.) Exerts Anti-Inflammatory Activity on Primary Human Monocytes-Macrophages. Foods. 2022 Aug 7;11(15):2366. doi: 10.3390/foods11152366. PMID: 35954130; PMCID: PMC9367727. Accessed 16 Oct. 2023.
13. Rezapour-Firouzi S, Kheradmand F, Shahabi S, Tehrani AA, Mazloomi E, Mohammadzadeh A. Regulatory effects of hemp seed/evening primrose oil supplement in comparison with rapamycin on the expression of the mammalian target of rapamycin-complex 2 and interleukin-10 genes in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Res Pharm Sci. 2019 Feb;14(1):36-45. doi: 10.4103/1735-5362.251851. PMID: 30936931; PMCID: PMC6407336. Accessed October 16, 2023.
14. Ice) R. 6 Evidence-Based Health Benefits of Hemp Seeds. Healthline. Published September 11, 2018. Accessed October 16, 2023.
15. Crichton-Stuart C. Health benefits of hemp seeds. Medicalnewstoday.com. Published September 11, 2018. Accessed October 16, 2023.
16. How can hemp seeds help women in different ways. Hampa Wellness. Published 2023. Accessed October 17, 2023.
17. SNS. How hemp is helpful for women in periods. The Statesman. Published January 27, 2021. Accessed October 17, 2023.
18. Griscti C. The Benefits of Hemp Seeds and Hemp Seed Oil. VITAL+ Pharmacy. Published May 14, 2021. Accessed October 17, 2023.
19. Ice) R. 6 Evidence-Based Health Benefits of Hemp Seeds. Healthline. Published September 11, 2018. Accessed October 17, 2023.
20. Maurotti S, Mare R, Pujia R, Ferro Y, Mazza E, Romeo S, Pujia A, Montalcini T. Hemp Seeds in Post-Arthroplasty Rehabilitation: A Pilot Clinical Study and an In Vitro Investigation. Nutrients. 2021 Nov 30;13(12):4330. doi: 10.3390/nu13124330. PMID: 34959882; PMCID: PMC8709006. Accessed October 17, 2023.
21. Farì G, Megna M, Scacco S, Ranieri M, Raele MV, Chiaia Noya E, Macchiarola D, Bianchi FP, Carati D, Panico S, Di Campi E, Gnoni A, Scacco V, Inchingolo AD, Qorri E, Scarano A, Rapone B. Hemp Seed Oil in Association with β-Caryophyllene, Myrcene and Ginger Extract as a Nutraceutical Integration in Knee Osteoarthritis: A Double-Blind Prospective Case-Control Study. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Jan 18;59(2):191. doi: 10.3390/medicina59020191. PMID: 36837393; PMCID: PMC9960141. Accessed October 17, 2023.
22. Crichton-Stuart C. Health benefits of hemp seeds. Medicalnewstoday.com. Published September 11, 2018. Accessed October 16, 2023.
23. Cerino P, Buonerba C, Cannazza G, D’Auria J, Ottoni E, Fulgione A, Di Stasio A, Pierri B, Gallo A. A Review of Hemp as Food and Nutritional Supplement. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2021 Feb 12;6(1):19-27. doi: 10.1089/can.2020.0001. PMID: 33614949; PMCID: PMC7891210. Accessed October 16, 2023.
24. Hemp Seed Oil Properties – Oklahoma State University. Published October 22, 2020. Accessed October 16, 2023.
25. Cerino P, Buonerba C, Cannazza G, D’Auria J, Ottoni E, Fulgione A, Di Stasio A, Pierri B, Gallo A. A Review of Hemp as Food and Nutritional Supplement. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2021 Feb 12;6(1):19-27. doi: 10.1089/can.2020.0001. PMID: 33614949; PMCID: PMC7891210. Accessed October 16, 2023.
26. Dresden D. 9 hemp seed oil products for hair growth, health, and repair. Medicalnewstoday.com. Published August 6, 2020. Accessed October 16, 2023.
27. Frothingham S. Hemp Seed Oil for Hair. Healthline. Published January 11, 2019. Accessed October 16, 2023.
28. Cannabidiol (CBD): What you need to know before you try it | Cedars-Sinai. Cedars-sinai.org. Published 2019. Accessed October 17, 2023.
29. Mlost J, Bryk M, Starowicz K. Cannabidiol for Pain Treatment: Focus on Pharmacology and Mechanism of Action. Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 23;21(22):8870. doi: 10.3390/ijms21228870. PMID: 33238607; PMCID: PMC7700528. Accessed October 17, 2023.
30. CBD for Arthritis Pain: What You Should Know. Arthritis.org. Published 2021. Accessed October 17, 2023.
31. Blessing EM, Steenkamp MM, Manzanares J, Marmar CR. Cannabidiol as a Potential Treatment for Anxiety Disorders. Neurotherapeutics. 2015 Oct;12(4):825-36. doi: 10.1007/s13311-015-0387-1. PMID: 26341731; PMCID: PMC4604171.
32. Can CBD Help with My Anxiety and Depression? | Anxiety and Depression Association of America, ADAA. Adaa.org. Published 2019. Accessed October 17, 2023.
33. gilmerm. Does CBD Help With Anxiety? Cleveland Clinic. Published April 28, 2022. Accessed October 17, 2023.
34. Ferguson S. All About CBD for Anxiety. Psych Central. Published June 4, 2021. Accessed October 17, 2023.
35. Advocacy: Medical Cannabis CBD. Epilepsy Foundation. Published 2022. Accessed October 17, 2023.
36. Medical Marijuana. Epilepsy Foundation. Published 2018. Accessed October 17, 2023.
37. CBD Products May Help People with Epilepsy Better Tolerate Anti-Seizure Medications. Johns Hopkins Medicine Newsroom. Published August 11, 2021. Accessed October 17, 2023.
38, Silvestro S, Mammana S, Cavalli E, Bramanti P, Mazzon E. Use of Cannabidiol in the Treatment of Epilepsy: Efficacy and Security in Clinical Trials. Molecules. 2019 Apr 12;24(8):1459. doi: 10.3390/molecules24081459. PMID: 31013866; PMCID: PMC6514832. Accessed October 17, 2023.
39. Golub V, Reddy DS. Cannabidiol Therapy for Refractory Epilepsy and Seizure Disorders. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1264:93-110. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-57369-0_7. PMID: 33332006. Accessed October 17, 2023.
40. neurocenternj. CBD for Seizures- Use, Effectiveness, Side Effects, and More. Neurology Center For Epilepsy & Seizures. Published May 10, 2021. Accessed October 17, 2023.
41. Fernández-Ruiz J, Sagredo O, Pazos MR, García C, Pertwee R, Mechoulam R, Martínez-Orgado J. Cannabidiol for neurodegenerative disorders: important new clinical applications for this phytocannabinoid? Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2013 Feb;75(2):323-33. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2012.04341.x. PMID: 22625422; PMCID: PMC3579248. Accessed October 17, 2023.
42. Aychman MM, Goldman DL, Kaplan JS. Cannabidiol’s neuroprotective properties and potential treatment of traumatic brain injuries. Front Neurol. 2023 Feb 2;14:1087011. Accessed October 17, 2023.
43. Maroon J, Bost J. Review of the neurological benefits of phytocannabinoids. Surg Neurol Int. 2018 Apr 26;9:91. doi: 10.4103/sni.sni_45_18. PMID: 29770251; PMCID: PMC5938896. Accessed October 17, 2023.
44. Kim J, Choi JY, Seo J, Choi IS. Neuroprotective Effect of Cannabidiol Against Hydrogen Peroxide in Hippocampal Neuron Culture. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2021 Feb 12;6(1):40-47. Accessed October 17, 2023.
45. Muhammad F, Liu Y, Wang N, Zhao L, Zhou Y, Yang H, Li H. Neuroprotective effects of cannabidiol on dopaminergic neurodegeneration and α-synuclein accumulation in C. elegans models of Parkinson’s disease. Neurotoxicology. 2022 Dec;93:128-139. Accessed October 17, 2023.
46. Campos AC, Fogaça MV, Sonego AB, Guimarães FS. Cannabidiol, neuroprotection and neuropsychiatric disorders. Pharmacol Res. 2016 Oct;112:119-127. Accessed October 17, 2023.
47. Lowin T, Ren T, Zurmahr J, Claßen T, Schneider M, Pongratz G. Cannabidiol (CBD): a killer for inflammatory rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts. Cell Death and Disease. 2020;11(8). Accessed October 17, 2023.
48. Atalay S, Jarocka-Karpowicz I, Skrzydlewska E. Antioxidative and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Cannabidiol. Antioxidants (Basel). 2019 Dec 25;9(1):21. doi: 10.3390/antiox9010021. PMID: 31881765; PMCID: PMC7023045. Accessed October 17, 2023.
49. Is Cannabidiol a Safe and Effective Sleep Aid? | Sleep Foundation. Sleep Foundation. Published May 4, 2021. Accessed October 17, 2023.
50. Ranum RM, Whipple MO, Croghan I, Bauer B, Toussaint LL, Vincent A. Use of Cannabidiol in the Management of Insomnia: A Systematic Review. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2023 Apr;8(2):213-229. doi: 10.1089/can.2022.0122. Epub 2022 Sep 23. PMID: 36149724. Accessed October 17, 2023.
51. Hanuš LO, Hod Y. Terpenes/Terpenoids in Cannabis: Are They Important? Med Cannabis Cannabinoids. 2020 Aug 10;3(1):25-60. doi: 10.1159/000509733. PMID: 34676339; PMCID: PMC8489319. Accessed October 17, 2023.
52. Does CBD Help With Sleep? – Sleep Doctor. Sleep Doctor. Published December 13, 2022. Accessed October 17, 2023.
53. McKeon R, Rittenberg E. Why are women using CBD products — and do they work? – Harvard Health. Harvard Health. Published November 18, 2019. Accessed October 17, 2023.
54. Melas PA, Scherma M, Fratta W, Cifani C, Fadda P. Cannabidiol as a Potential Treatment for Anxiety and Mood Disorders: Molecular Targets and Epigenetic Insights from Preclinical Research. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 13;22(4):1863. doi: 10.3390/ijms22041863. PMID: 33668469; PMCID: PMC7917759. Accessed October 17, 2023.
55. Pinto JV, Saraf G, Frysch C, Vigo D, Keramatian K, Chakrabarty T, Lam RW, Kauer-Sant’Anna M, Yatham LN. Cannabidiol as a Treatment for Mood Disorders: A Systematic Review. Can J Psychiatry. 2020 Apr;65(4):213-227. doi: 10.1177/0706743719895195. Epub 2019 Dec 13. PMID: 31830820; PMCID: PMC7385425. Accessed October 17, 2023.
56. Batalla A, Bos J, Postma A, Bossong MG. The Impact of Cannabidiol on Human Brain Function: A Systematic Review. Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jan 21;11:618184. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.618184. PMID: 33551817; PMCID: PMC7858248. Accessed October 17, 2023.
57. Brugnatelli V, Turco F, Freo U, Zanette G. Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Manipulating the Endocannabinoid System as First-Line Treatment. Front Neurosci. 2020 Apr 21;14:371. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.00371. PMID: 32372912; PMCID: PMC7186328.
58. Fletcher J. Can people use CBD for irritable bowel syndrome? Medicalnewstoday.com. Published January 28, 2021. Accessed October 17, 2023.
59. Coelho S. CBD for IBS: Does It Work? Healthline. Published January 25, 2021. Accessed October 17, 2023. https://www.healthline.com/health/cbd-for-ibs#can-it-help#:~:text=Doctors%20sometimes,CBD.
60. Pinto JS, Martel F. Effects of Cannabidiol on Appetite and Body Weight: A Systematic Review. Clin Drug Investig. 2022 Nov;42(11):909-919. doi: 10.1007/s40261-022-01205-y. Epub 2022 Oct 1. PMID: 36180814; PMCID: PMC9525229. Accessed October 17, 2023.
61. CBD: Safe and effective? Mayo Clinic. Published 2022. Accessed October 17, 2023.
62. Johnson J. Can CBD help you lose weight? Medicalnewstoday.com. Published March 19, 2019. Accessed October 17, 2023.
63. Nichols JM, Kaplan BLF. Immune Responses Regulated by Cannabidiol. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2020 Feb 27;5(1):12-31. doi: 10.1089/can.2018.0073. PMID: 32322673; PMCID: PMC7173676.
64. Martini S, Gemma A, Ferrari M, Cosentino M, Marino F. Effects of Cannabidiol on Innate Immunity: Experimental Evidence and Clinical Relevance. Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 4;24(4):3125. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043125. PMID: 36834537; PMCID: PMC9964491.
65. Cannabidiol inhibits SARS-CoV-2 replication through induction of the host ER stress and innate immune responses. Science Advances. Published 2022. Accessed October 18, 2023.
Baswan SM, Klosner AE, Glynn K, Rajgopal A, Malik K, Yim S, Stern N. Therapeutic Potential of Cannabidiol (CBD) for Skin Health and Disorders. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2020 Dec 8;13:927-942. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S286411. PMID: 33335413; PMCID: PMC7736837. Accessed October 17, 2023.
Makhakhe L. Topical cannabidiol (CBD) in skin pathology – A comprehensive review and prospects for new therapeutic opportunities. S Afr Fam Pract (2004). 2022 May 30;64(1):e1-e4. doi: 10.4102/safp.v64i1.5493. PMID: 35695447; PMCID: PMC9210160. Accessed October 17, 2023.
Rosanna Turner Should I Use CBD Products on My Skin? | Cedars-Sinai. Cedars-sinai.org. Published 2020. Accessed October 17, 2023.
Morales-Brown L. Is CBD oil good for skin? Medicalnewstoday.com. Published January 15, 2021. Accessed October 17, 2023.
